Power Inverters : Everything You Need to Know About
When the Lights Go Out, Knowledge Becomes Power
Picture this: you’re working on something important or enjoying a quiet evening when the electricity suddenly vanishes. You’re left staring into the dark, frustrated, and unprepared. It’s a feeling too many people know—but it doesn’t have to be yours. Power inverters are your silent allies in times like this, giving you reliable electricity from sources you control. Whether you’re living off-grid, planning for emergencies, or simply want more control over your energy use, understanding power inverters isn’t just useful—it’s essential.
Let’s walk through everything you need to know so that next time the power drops, you don’t.
Table of Contents
What Is a Power Inverter and Why Should You Care?
The Basics in Simple Terms
A power inverter is a device that transforms direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is the kind of electricity your appliances use. Without this conversion, your fridge, TV, or laptop wouldn’t function during an outage or when you’re off the grid.
If you’ve ever used a solar setup or car battery charger, you’ve likely relied on an inverter without realizing it.
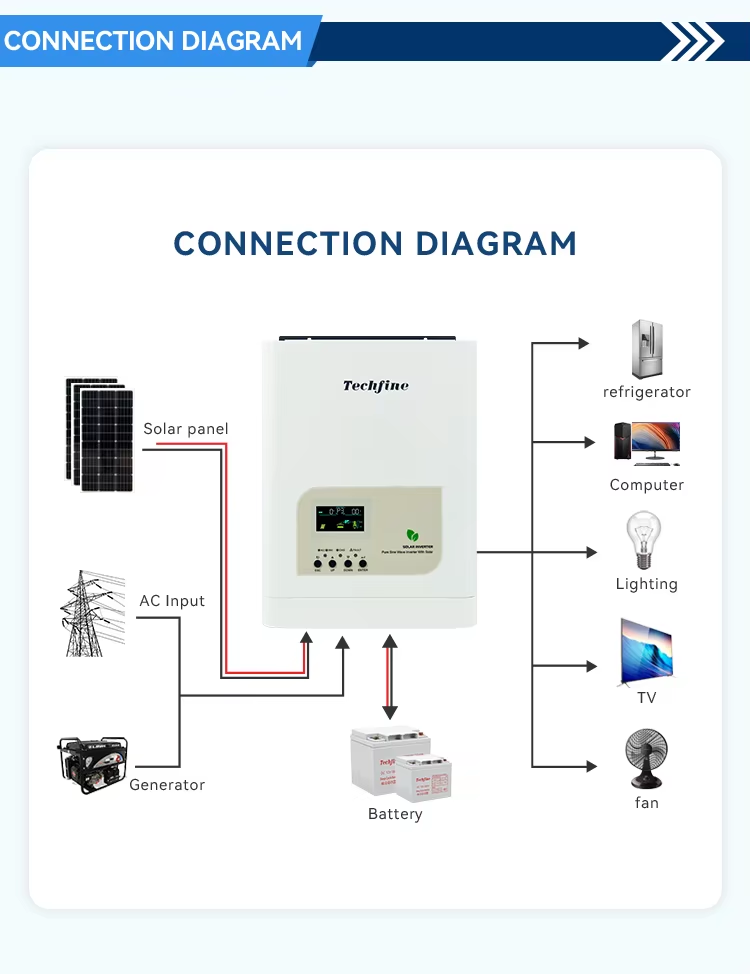
How It Works Behind the Scenes
Here’s the short version:
- Batteries produce DC power (steady and unidirectional).
- Most home electronics run on AC power (alternates directions).
- A power inverter converts that DC into usable AC.
It’s like translating a language your devices can understand.
Types of Power Inverters: Which One Matches Your Needs?
Not all inverters are created equal, and choosing the wrong type can leave you disappointed—or worse, in the dark. Here’s what you need to know:
1. Pure Sine Wave Inverters
These are the top-shelf models. They produce a clean, smooth, and stable current that’s safe for any device—especially sensitive ones like CPAP machines, gaming consoles, or LED TVs.
Pros:
- Efficient and reliable
- Perfect for homes and medical equipment
- Safe for all electronics
Cons:
- Pricier than other options
2. Modified Sine Wave Inverters
A budget-friendly middle ground. These deliver electricity in a more “stepped” pattern, which isn’t ideal for high-end electronics but works for simpler tools and appliances.
Pros:
- Affordable
- Great for simple tasks (fans, lights, power tools)
Cons:
- May cause noise or reduced performance in sensitive devices
3. Square Wave Inverters
These are outdated and rarely used now. They create choppy power that’s not suitable for most modern devices. Skip these unless you’re powering old-school equipment.
Side-by-Side Comparison Table
| Inverter Type | Efficiency | Ideal For | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Sine Wave | High | Sensitive electronics, homes | $$$ |
| Modified Sine Wave | Medium | Basic appliances, tools | $$ |
| Square Wave | Low | Obsolete systems | $ |
Must-Have Features in a Power Inverter
If you’re investing in an inverter, don’t just go for the cheapest or flashiest. Look at the features that actually matter.
Power Capacity
- Continuous power: What it can deliver steadily
- Surge power: What it can handle temporarily (e.g., fridge starting up)
Tip: Always oversize your inverter by 20–30% based on your device needs.
Safety Mechanisms
A good inverter protects itself—and your devices.
✔ Overload protection
✔ Short-circuit safety
✔ Low battery shutdown
✔ Overheating alerts
Usability Features
The best inverter won’t make you feel like a technician. Look for:
- Digital display for voltage/wattage
- Remote control (especially for fixed setups)
- USB ports for mobile charging
- Quiet operation
Where and How You Can Use Power Inverters
You might think inverters are only for power outages. But once you realize how versatile they are, you’ll want one for almost every setup.
Home Backup Systems
Whether you’re facing blackouts or unreliable service, an inverter can keep your essentials running—lights, Wi-Fi, fridge, even medical equipment.
Solar Power Integration
In solar setups, inverters are non-negotiable. They take the DC power your solar panels generate and make it usable for your entire home.
RV, Camping & Van Life
Take your home comforts on the road. An inverter turns your car battery or solar bank into a mini power station.
Remote Work Sites
Construction, outdoor projects, mobile services—all benefit from an inverter that powers tools when no wall plug is in sight.
Choosing the Right Inverter: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. List What You’ll Power
Start with a complete list of devices you want to use. Include surge ratings for things like fridges or pumps.
2. Add Up Wattage
Add their wattage, then add 25% for safety margin. That’s your minimum inverter size.
3. Decide on Type
If you plan to run laptops, TVs, or anything digital, lean toward pure sine wave. If you just need to run lights or basic tools, a modified wave may be enough.
4. Choose Voltage
Match your battery setup: 12V for cars, 24V for larger systems, etc.
5. Read Real Reviews
Don’t fall for specs alone. Look for real-world usage reviews, especially for reliability and noise.
Installing and Maintaining Your Power Inverter
You don’t need to be an engineer to get this right, but you do need to be careful.
DIY or Pro?
- DIY Installation: Safe for plug-and-play models with built-in protection
- Professional Install: Recommended for large home or solar systems
Placement Tips
- Keep it dry and well-ventilated
- Avoid closed boxes or tight spaces
- Mount securely to avoid vibration damage
Maintenance Checklist
✅ Inspect cables monthly
✅ Test inverter output quarterly
✅ Clean battery terminals
✅ Replace worn fuses or connectors
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Sometimes inverters act up. Here’s how to fix them fast:
Problem: Inverter Won’t Turn On
- Check the battery charge
- Inspect fuse or wiring
Problem: Loud Alarm or Beeping
- Often a low battery warning
- Could also indicate overload
Problem: Overheating
- Ensure proper ventilation
- Fan may be blocked or broken
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What size inverter do I need to run a house?
To power essentials like a fridge, lights, and router, you’ll need at least a 2000W pure sine wave inverter. For full home coverage, 4000W+ is more realistic.
Can an inverter run air conditioning or a washing machine?
Yes, but only if it supports high surge loads. Always check the startup wattage of those devices before choosing.
Is it safe to leave my inverter on 24/7?
Most quality inverters are designed for continuous use. Just ensure they’re in a cool space and not overloaded.
Do I need a special battery?
Deep-cycle batteries (AGM, lithium) are best. They discharge slowly and last longer—perfect for inverters.
What’s better: inverter or generator?
Inverters are quiet, clean, and safe for electronics. Generators provide more power but require fuel and create noise. Use both for a balanced setup.
Conclusion: Make Power One Less Thing to Worry About
In an increasingly uncertain world, having control over your energy isn’t just smart—it’s empowering. With the right power inverter, you’re no longer at the mercy of the grid or the elements. You can live, work, travel, and stay safe wherever you are.
From selecting the best type to knowing how to install and use it properly, you’re now equipped with everything you need to make informed choices. Don’t wait for the next blackout to get prepared—start taking charge of your power today.

